The Fool and His Money: Mainline Puzzle Specifics
By now, I’ve finished all of the main-sequence puzzles, which is more than I managed back in 2012. As the last few in the list got marked as solved, I started thinking that I was almost done with the game, but this turned out not to be the case. I knew there would be a metapuzzle involving arranging tiles to form a map with the final wave of puzzles on it, because that’s how The Fool’s Errand ended, and the map itself had been accessible, if incomplete, throughout the game. But the map is a great deal more involved this time around, less a finale and more a final act. I still have a way to go.
So let’s take a close look at what I’ve just been through. Ignoring the sneaky “Seventh House” stuff, there are 70 puzzles in the main list, in four groups associated with the Tarot suits. Each is indicated by a name — not a name that describes the puzzle, but a person’s name, like “Ursula” or “Crichton”, which seems to be linked to people forgetting their names in the story. When two names start with the same initial, the associated puzzles are the same type.
Five of the puzzles are card games, using Tarot deck variations with some extra cards referencing the story. There was one puzzle like this in Errand, but it was one of the more satisfying things in the game, so I’m pleased to see it expanded into a genre. The basic idea in all of them is that you and an opponent take turns swapping cards between your hand and a common pool, trying to make combos that score points. But the rules beyond that, and what the combos are, are things you have to figure out by observation.
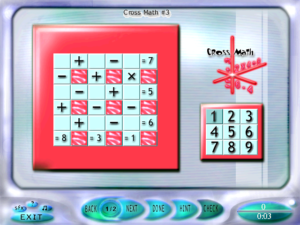
Nine are tile-based picture-assembly puzzles of various sorts. Four are memorization puzzles where you trace a specific path through the irregular panes of a stained glass window. Three involve arranging tiles with numeric values to create specific sums. One is the perennial sort where you have to create a specific configuration of a group of things by pressing buttons, each of which cycles a different subset of the things through different states. One particularly difficult one is a rule-guessing game reminiscent of Petals Around the Rose: given six coins with various faces, you have to figure out how to tell which two to flip over to reveal the same symbol. The rule here doesn’t make physical sense, but it’s completely consistent and predictable once you know how to do it.
The remaining 47 puzzles are all about making words and sentences in various ways.
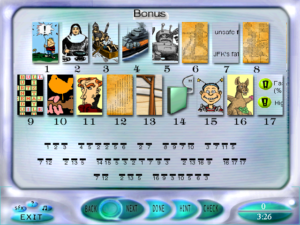
Mostly this means unscrambling letters. For example, there’s a set of puzzles that give you 4×4 grids of letters, which you have to rearrange so that every row and column is a word. Another type gives you a stack of bands of letters, which you shift left and right to form words in a highlighted central column. An interesting special case: Any puzzle that produces seven-letter words will feed them into a later puzzle, which you therefore can’t solve until you’ve completed the earlier ones. This is the game’s first real hint of metapuzzlery.
There’s some redundancy: there’s a set of cryptograms, but there’s also a set of puzzles where you select letters out of a list to make multiple copies of the letter appear in an expanding sequence that sprouts punctuation as you go, and after you’ve tried this a few times, you realize that it’s just a cryptogram in disguise, with a less convenient interface.
I mentioned a puzzle where you press buttons to cycle objects through different states. Well, there’s three others where you do the same thing, except the objects are letters in a word. This is a bigger change in the nature of the puzzle than it sounds like, because it’s not clear what the target word is. Interestingly, this means solving the puzzle effectively has two phases, figuring out what word you can make from the given letters and figuring out how to use the available buttons to produce it, even though there’s no separation of phases in its implementation.
Another notable type: the letter auctions. You have a bunch of letters, and there’s a bunch of potential buyers trying to turn four-letter sets into five-letter words. Your challenge is to optimize your earnings by auctioning your letters in the right order. Satisfy a customer too early, and they won’t be around to pump up the bidding on later letters. Now, this seemed to me at first to be essentially a math problem. By observation, I could learn each bidder’s maximum bid and derive the maximum value of each letter and so forth. But the behavior of the bidders is complicated and perhaps unpredictable — I’m sure I’ve sometimes seen people bidding on letters they couldn’t actually use. Ultimately, the key was to not try to figure it out that way. All that really matters is that all the words in the optimal solution fit a theme, and that by hitting “Undo” whenever someone makes a wrong word, you can backtrack your way to the solution. I’m pretty sure that the word auctions were among the puzzles I didn’t manage to solve last time, and I can’t say I like them much.
One peculiar thing about the words you make: Since the setting is based on Tarot, it’s all sort of vaguely pre-industrial. This is a land of kings and queens, swords and wands, hermits and heirophants. And this puts limits on the game’s vocabulary. So if one of those 4×4 word grids can make the word “cola”, for example, you know that it’s not going to be part of the solution. But those grids keep track of how many words you have — the cash offer for the grid increases with each word — and thus you can see that “cola” is counted as a word even so.
 Comments(0)
Comments(0)